
Seeing your once-healthy plants develop a dusty, orange coating can be truly alarming. This is the tell-tale sign of leaf rust, a common and stubborn fungal disease that can make plants look sick and weak. It feels like the plant is literally rusting away, and the frustration for a gardener is immense. This guide is here to reassure you that you can fight back. We’ll explore what leaf rust is, how to spot it early, and the proven methods to control it, helping you restore the health and beauty of your plants.
What is leaf rust & why is it a concern for plants?
Leaf rust is a term for a group of fungal diseases caused by various species of fungi, most notably from the Puccinia genus. It gets its name from the powdery, rust-colored pustules that form on the infected parts of the plant, primarily the leaves.
It is a global concern because it affects a vast range of plants, from major agricultural crops to common garden ornamentals. Some well-known hosts include:
- Cereal grains: Wheat, barley, and rye.
- Commercial crops: Coffee, sugarcane, and soybeans.
- Garden plants: Snapdragons, roses, hollyhocks, and leeks.
- Trees: Pear and poplar trees.
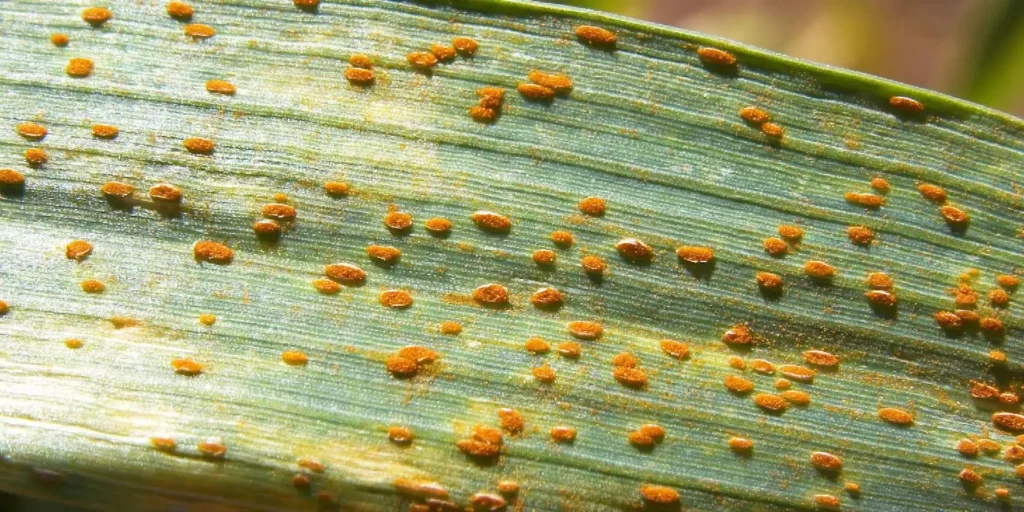

The disease is a serious problem because it directly attacks the plant’s ability to create food. By covering the leaf surface, it reduces photosynthesis, stresses the plant, and can lead to significant yield losses in crops and an overall decline in the health and appearance of ornamental plants.
What causes leaf rust & how does it spread?
Leaf rust diseases are caused by highly specialized pathogenic fungi. The specific pathogen often depends on the host plant; for example, wheat leaf rust is caused by Puccinia triticina, while coffee leaf rust is caused by Hemileia vastatrix.
These fungi thrive in specific environmental conditions, with prolonged leaf wetness and moderate temperatures (typically 16–24°C) being the key triggers for infection.
The spores are microscopic and spread with incredible efficiency. They are easily carried over long distances by wind currents, but also spread locally through rain splash and on contaminated tools, clothing, or hands.
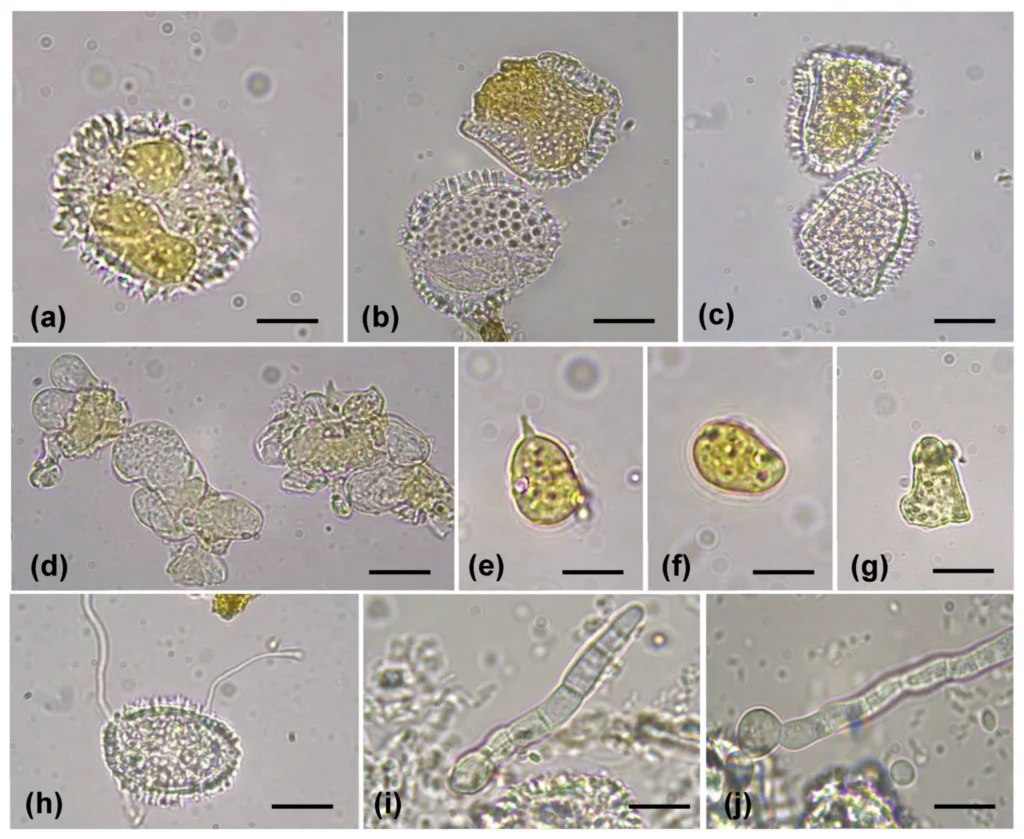
H. vastatrix produces different spore types: (a–c) uredospores responsible for rapid disease spread, (d–g) teliospores with or without papillae, and (h–j) germinating spores. These structures are microscopic, with scale bars representing just 10 µm.
How can you identify leaf rust symptoms early?
Early detection is crucial for managing leaf rust. The symptoms often start subtly but develop into very distinct characteristics. Keep an eye out for the following signs:
- Initial spots: The first clue is often the appearance of small, pale yellow or light green spots, usually on the underside of the leaves.
- Pustule development: These spots soon develop into raised blisters or pustules. These pustules eventually break through the leaf surface, releasing masses of powdery spores.
- Color variation: The color of the spores is the most defining feature and can be yellow, orange, reddish-brown (like rust), or even black, depending on the rust species and the stage of its life cycle.
- The “rub-off” test: A simple way to confirm rust is to gently rub one of the pustules with your finger. The powdery spores will come off easily, leaving a colored smudge on your skin, similar to touching a rusty piece of metal.
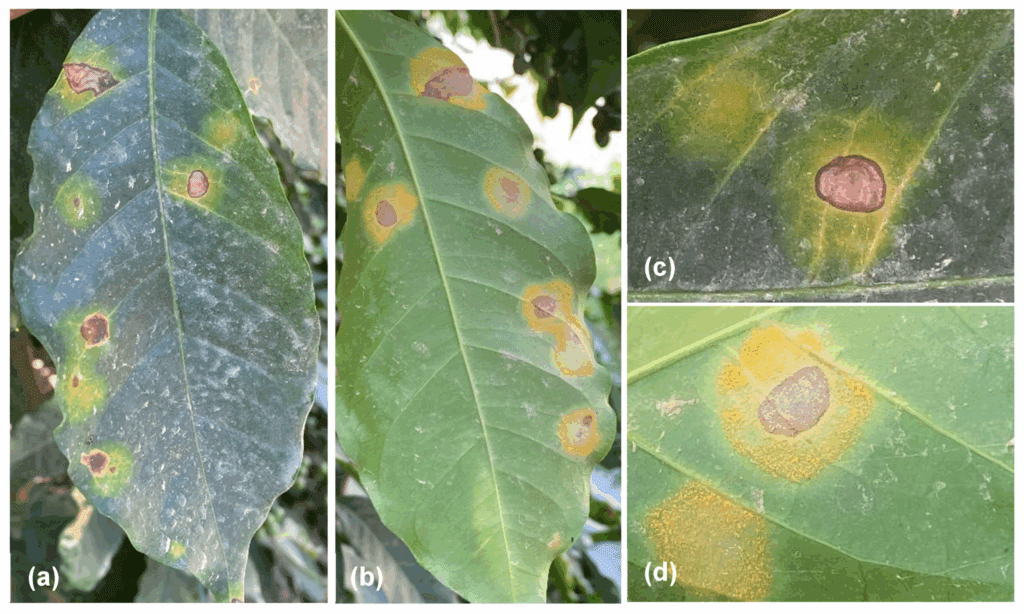
(a) Coffee leaf rust on the upper surface shows round, yellow-orange spots
(b) Lower surface displays powdery orange lesions
(c) Close-up of upper lesions with necrotic tissue
(d) Close-up of underside with powdery uredospores
It’s important to distinguish leaf rust from other diseases. Leaf rust typically forms distinct, powdery pustules, whereas other leaf spots might be flat, and blights often cause larger, water-soaked lesions that lead to rapid tissue death.
What is the impact of leaf rust on plant health and yield?
Leaf rust is more than just a cosmetic problem; it’s a direct assault on the plant’s vitality. By covering the leaves with pustules, the disease significantly reduces the available surface area for photosynthesis, which is how the plant produces its energy.
This leads to premature yellowing and leaf drop, further weakening the plant. In agricultural crops, the impact on yield can be devastating. Severe leaf rust epidemics have been known to cause yield losses ranging from 21% to 47% in susceptible wheat varieties. Under catastrophic conditions, some studies have reported potential losses of up to 50%. While the average annual global loss in wheat is estimated to be lower, local outbreaks can still have a massive economic impact.
How can you prevent and manage leaf rust effectively?
A combination of good cultural practices and timely intervention is the best strategy for controlling leaf rust.
| Management strategy | Action steps |
| Sanitation | Remove and destroy infected leaves and plant debris at the end of the season to reduce overwintering spores. |
| Improve airflow | Space plants properly and prune any overhanging trees or dense foliage to allow leaves to dry quickly. |
| Smart watering | Water at the base of the plant to avoid wetting the leaves. Water in the morning so foliage has time to dry. |
| Resistant varieties | Choose plant varieties that are specifically bred for resistance to rust diseases. This is the most effective long-term solution. |
| Crop rotation | For vegetables like leeks, avoid planting them in the same spot each year. |
| Fertilization | Avoid high-nitrogen fertilizers that encourage soft, susceptible growth. Use high-potash feeds to help strengthen plants. |
| Fungicides | For severe or persistent infections, apply approved fungicides preventively or at the first sign of disease. Follow label instructions carefully. |
What role do resistant plant varieties play in controlling leaf rust?
Utilizing resistant plant varieties is considered the most effective, economical, and environmentally friendly strategy for managing leaf rust, especially in agriculture.
Plant breeders have worked for decades to develop cultivars with strong genetic resistance. For example, wheat cultivars like Misr-2 and Giza-171 have shown high levels of resistance to common leaf rust races. In the coffee industry, the development of rust-resistant varieties like Batian and Arara has been crucial for the sustainability of coffee farming, as they not only resist the disease but also produce high-quality beans.
An integrated strategy that combines resistant varieties with smart cultural practices provides the most durable and long-lasting protection against this persistent disease.
Conclusion
In the end, while discovering leaf rust on your plants is frustrating, it’s a battle you can win with knowledge and proactive care. Creating a healthy garden environment and choosing the right plants are your strongest defenses.
For a modern tool to assist you, the Planteyes app is excellent for helping you identify disease symptoms from a simple photo. You can also chat with an in-app expert to get personalized advice, giving you the confidence to take the right action. Download it today and keep your plants thriving and rust-free.
FAQs
Can leaf rust spread to other types of plants in my garden?
Generally, no. Rust fungi are often highly specialized and host-specific. This means the rust affecting your roses will not infect your wheat, and the rust on your leeks won’t spread to your snapdragons.
Is it possible to treat leaf rust without chemicals?
Yes. Effective organic management relies on strict sanitation (removing infected leaves), improving air circulation, proper watering, and, most importantly, planting resistant varieties.
How quickly does leaf rust develop after infection?
After a spore infects a leaf, there is a latent period where the fungus grows inside the tissue without showing symptoms. This can last from seven days to several weeks, after which the visible pustules will appear.
What weather conditions make leaf rust outbreaks more likely?
Outbreaks are most common during periods of high humidity and moderate temperatures (16–24°C), especially when leaves remain wet for many hours from rain, dew, or overhead irrigation.
Are there plant disease identification apps that can detect leaf rust?
Yes, modern apps like Planteyes can analyze photos of your plants to help you identify the distinct, powdery pustules characteristic of leaf rust, allowing for early detection and management.
