
Seeing ugly, discolored spots spreading across the vibrant leaves of your plants can be incredibly frustrating for any gardener. This common problem is often a sign of fungal leaf spot, a disease that can quickly spoil the beauty and health of your garden. While it may feel discouraging, you are not helpless in this fight. This guide is here to help you understand what causes these spots, how to recognize them early, and the best ways to treat and prevent them, ensuring your plants stay healthy and beautiful.
What is fungal leaf spot & why does it matter?
Fungal leaf spot is not a single disease but a broad category of plant diseases caused by a huge variety of different fungi. These diseases all share a common symptom: they produce spots on the foliage of infected plants.
It is an incredibly common problem, affecting a vast range of plants, including everyday vegetables like tomatoes and cucumbers, fruit trees like apples and cherries, and countless ornamentals such as roses, hydrangeas, and maples.
While a minor case might only be a cosmetic issue, a severe infection is a serious concern. It can lead to significant leaf drop, which reduces the plant’s ability to photosynthesize, weakening its overall health. This can result in reduced growth, lower fruit or flower yield, and make the plant more vulnerable to other diseases and pests.
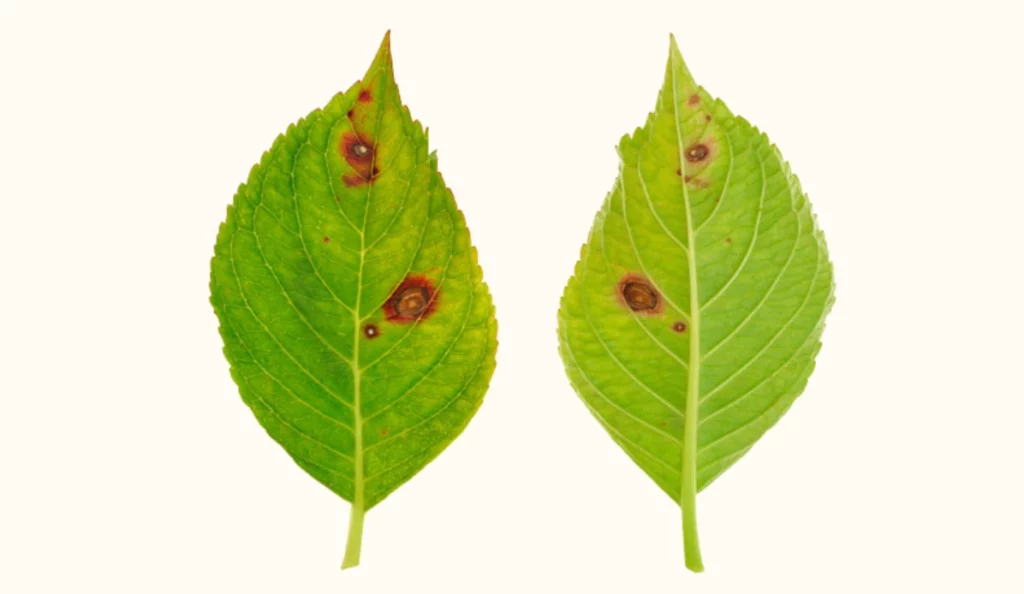

How can you identify fungal leaf spot symptoms?
The most obvious sign is, of course, spots on the leaves. However, the appearance of these spots can vary greatly depending on the specific fungus and host plant. Look for:
- Small, circular spots that can be brown, black, tan, or even reddish.
- Spots that may have a dark border or a yellow halo around them.
- In some cases, you might see tiny black dots within the spots, which are the fungal fruiting bodies.
- As the disease progresses, the spots may merge to form larger blotches or patches.
- Severely infected leaves often turn yellow and drop prematurely from the plant.
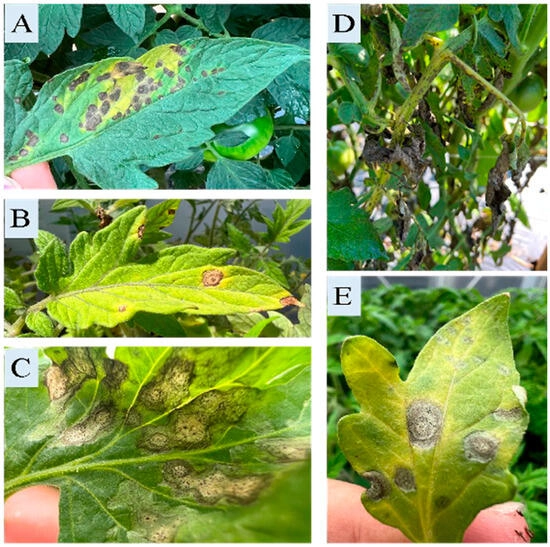
Symptoms of Septoria leaf spot on greenhouse-grown tomato in Mills River, NC: (A) Dark brown necrotic patches. (B) Gray-brown lesions with concentric rings. (C,E) Small dark pycnidia on infected leaf areas. (D) Severe infection affecting leaflets and stems.
What causes fungal leaf spot outbreaks?
Fungal leaf spot diseases don’t just happen; they are triggered by a specific set of environmental conditions that allow the fungal pathogens to flourish and infect plants. Understanding these causes is the first step toward prevention.
The primary driver for almost all fungal leaf spot diseases is prolonged moisture on the leaves. Fungal spores need a film of water to germinate and penetrate the leaf tissue. This is why outbreaks are most common during periods of rainy, humid weather.
Several factors contribute to creating these ideal conditions:
- Poor air circulation: When plants are spaced too closely together or are overgrown with dense foliage, air cannot move freely. This traps humidity and slows down the drying of leaves after rain or watering.
- Overhead watering: Sprinkling water over the top of plants is a major cause of leaf spot diseases. It wets the entire leaf surface, providing the perfect environment for fungal growth.
- Infected debris: Many of these fungi can survive the winter in fallen leaves and other plant debris. When conditions are right in the spring, spores are released from this debris to start a new cycle of infection.
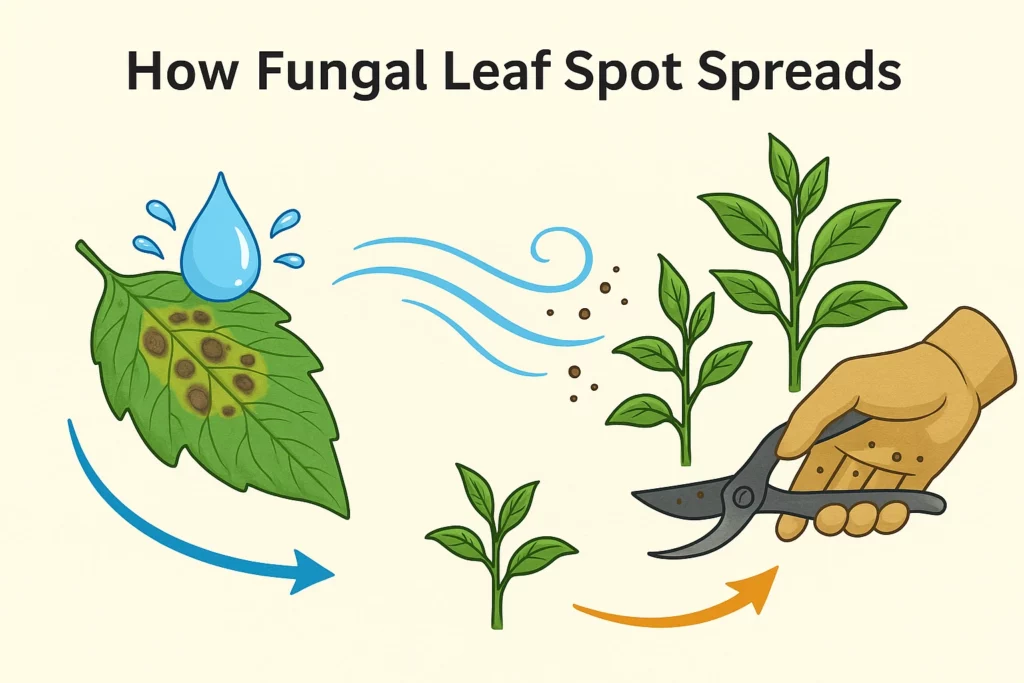
How does fungal leaf spot spread?
Fungal spores are microscopic and incredibly efficient at spreading throughout a garden. The most common method of transport is through water splash. When raindrops or irrigation water hit an infected leaf, it can splash spores onto nearby healthy leaves or even onto adjacent plants, spreading the disease locally.
Wind is another major carrier. The tiny, lightweight spores can become airborne and travel long distances on wind currents, introducing the disease to entirely new areas. You can also be an unwitting carrier. Spores can stick to your hands, clothing, and gardening tools, and you can easily transfer them from an infected plant to a healthy one as you work in your garden.
How can you treat fungal leaf spot?
Once an infection has started, the goal is to manage the disease and prevent it from spreading further.
| Treatment strategy | Action steps |
| Sanitation and pruning | Immediately remove and destroy any leaves that show signs of infection. Prune dense foliage to improve airflow. |
| Remove debris | Rake up and dispose of all fallen leaves and debris from around the base of the plant. Do not compost this material. |
| Organic fungicides | Apply copper-based or sulfur-based fungicides. Neem oil can also be effective in some cases. |
| Chemical fungicides | Use a fungicide labeled for the specific disease and plant type. Rotate different chemical groups to prevent resistance. |
How can you prevent fungal leaf spot in the future?
- Choose resistant varieties whenever possible.
- Ensure proper spacing between plants to promote good air circulation.
- Water the base of the plant in the morning to keep foliage dry.
- Apply a layer of mulch to prevent soil-borne spores from splashing onto leaves.
- Clean up all garden debris thoroughly at the end of the season.
- Disinfect your pruning tools between plants.
Conclusion
In the end, keeping fungal leaf spot under control is all about being a vigilant and proactive gardener. By minimizing leaf wetness and practicing good sanitation, you can create a garden where your plants thrive and diseases don’t.
For a modern tool to aid your efforts, the Planteyes app is wonderful for helping you identify the early signs of disease from a simple photo. Even better, you can chat with an in-app expert for personalized solutions, giving you confidence and clarity when you need it most. Download it today and give your plants the best defense possible.
FAQs
How can I tell fungal leaf spot from other leaf diseases?
Fungal leaf spots are typically round with distinct edges and may have fungal growth (tiny black dots) in the center. Bacterial spots often look more angular and water-soaked.
Can fungal leaf spot kill a plant?
It’s rare for leaf spot to kill a mature, healthy plant on its own. However, severe infections can cause major defoliation, which weakens the plant significantly and can make it susceptible to other fatal issues.
What plants are most susceptible to fungal leaf spot?
It varies widely, but many common plants like roses, tomatoes, hydrangeas, and maples are frequently affected by one or more types of leaf spot fungi.
How long can fungal leaf spot fungi survive in soil?
Most survive in infected plant debris on the soil surface for one to two years. This is why fall cleanup is so crucial for disease prevention.
Is there an app that can help me identify fungal leaf spot early?
Yes, plant care apps like Planteyes are designed to analyze photos of your plant’s leaves to help you identify the symptoms of fungal leaf spot, allowing for quicker diagnosis and treatment.
